The site is being updated.
- Join Us
-

- Georgian
Parliament starts a discussion of a legislative proposition on human companion animals
Recent frequent sadistic treatment of animals has once again demonstrated a need for an appropriate legislative basis.
Last year a legislative proposition on a new bill and amendments to the respective laws regarding the welfare of human companion animals was proposed by animal rights organizations[1] in the Parliament of Georgia.
The proposition aims to create protection guarantees for human companion animals[2]. A similar initiative was also registered in the previous, 8th Parliament[3], however, the discussions were terminated at the committee level.
What does the legislative proposition consider?
- Legal status of human companion animals is defined, as well as, conditions for their care and welfare, responsibilities, and duties of their owners, competencies of central and local governments in protection of welfare of such animals;
- Possibility for allocation of companion animals to a shelter is defined, as well as, appropriate conditions and standards at such shelters;
- Organization of animal fights, ritual killings, experimentation and surgical procedures without vet’s prescription are defined as criminal offenses;
- Amendments to administrative code define fines for transgression of rules of transportation of animals, rules for prevention of death of animals and other cases;
- Companion animals are subject to initial registration, identification and annual control registration, unified animal register will be created and conditions for care will be defined;
- According to the proposed amendments to the Code on Self Governance, the authority of local municipalities is expanded to include its authority over management and control of animal population;
- Temporary and long-term shelters are to be established on the territories of municipalities. Standards of these shelters are also defined. The shelters need to be equipped with an appropriate lab, veterinarian, quarantine, and walking spaces, as well as, living compartments, requirements for which are also defined.
Current legislation on animal cruelty
The existing legislation doesn’t define the concept of human companion animals or common standards for the protection of their rights.
The Criminal Code includes a regulation, according to which animal cruelty which results in death or mutilation of the animal, as well as, tormenting of animals are punished with a fine or community service up to 1 year. Same acts performed in a group, repetition of these acts, or conducting them in a presence of a minor are punishable by a fine or prison up to 2 years.
International Practice
Animal rights, in the international practice, are regulated using dedicated laws, as well as, through Criminal Code. Dedicated laws on protection of animal rights have been enacted in Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Croatia, Slovenia and etc.
For instance, in Austria[4], a person that inflicts pain, or puts an animal under intensive fear or kills an animal is fined 7 500 Euros, in case of a second offense - 15 000 Euros. In Belgium, abandonment of an animal and/or animal cruelty are punished with 1 to 3 months prison term, while same offenses in aggravating conditions can be punished with up to 3 years in prison[5].
Reactions to current cases
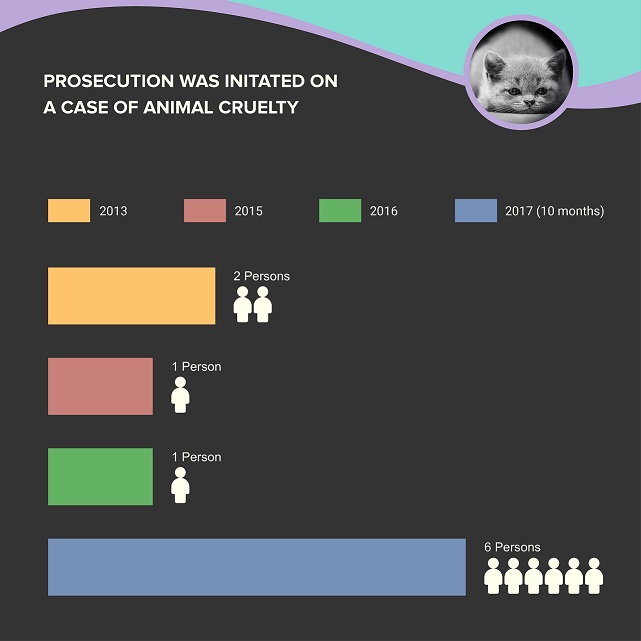
According to the data of the Ministry of Internal Affairs from 2010 to 2017 (10 months of the year), criminal prosecution was initiated in 8 cases of animal cruelty, and the court discussed only 5 cases. According to the information from the Prosecutor’s Office, in this period 10 people have been prosecuted.
Diagram 1. Ministry of Internal Affairs data on cases involving Article 259 of the Criminal Code in 2010-2017
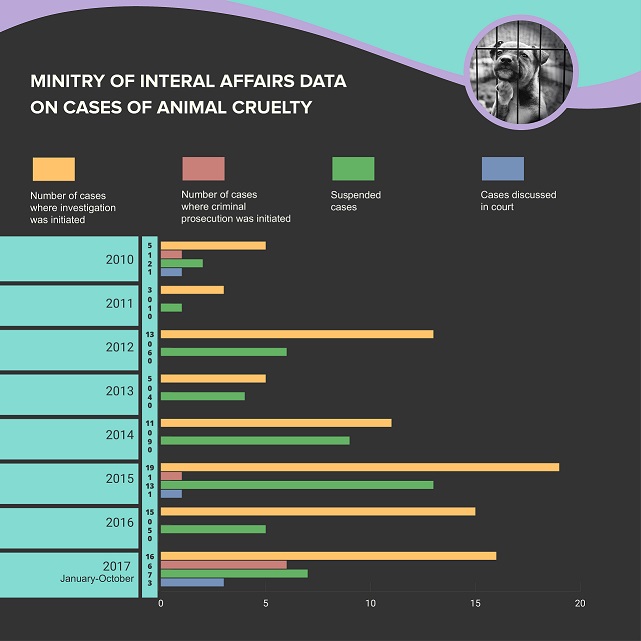
Diagram 2. Data of the Prosecutor’s Office on prosecution of cases involving Article 259 of the Criminal Code in 2010-2016 and 10 months of 2017
Transparency International Georgia believes the proposition is a positive step towards protection of animals. It is important that violations of this law be effectively addressed, and the stricter norms regarding animal cruelty are established and a unified legislative framework for the protection of animal rights is created.
This blog post was prepared as part of the project Strengthening Parliament Accountability and Transparency of its Activities within the framework of USAID program Good Governance Initiative in Georgia. Opinions expressed in this blog post belong to Transparency International Georgia and may not reflect the position of USAID or the Government of United States of America.
[1] Committee on Animal Rights; Animal Protection Organization Humanly; Animal Protection Organization of Georgia; Center for Animal Rights Advocacy.
[2] The proposal defines human companion animal as an animal that is kept by a human for esthetic or social needs; is to be cared by a human and isn’t used for production of food (including meat, milk or egg), fur, feather, leather or other animal products.
[3] Initiator: Member of the Parliament G. Tsagareishvili. Author: Committee on Animal Rights, Animal Protection Organization Humanly, Center for Social Programs and Development.
[4] Federal Act on the Protection of Animals (Animal Protection Act – TSchG) § 38 https://goo.gl/A41yJo
[5] Criminal Code of the Kingdom of Belgium, Section 161, https://goo.gl/eu5Wqo
My Parliament
Here you can find information about your representatives in Parliament and the decisions they make on your behalf.




